
Published at 10th Dec 2010
Modified at 1st Nov 2023
Ancient Greek Coin- Aegina's Turtle
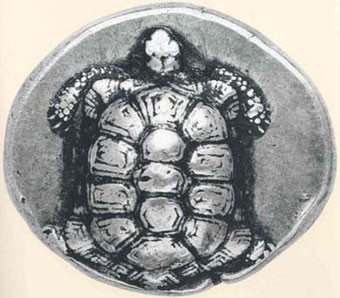
One of the most important coin of the Antiquity was the “Aegina’s turtle”. The coin itself is not very attractive as a first impression, yet it is one of the most important coins in history, with a same impact on the economical life of the Mediterranean Sea as the pound.
Aegina is an island in the Aegean Sea, on the East part of Greece. It was an important trade center in the area. It was the first city in Greek history that struck coins, around the middle of the seventh century or not long after that moment.
When the need for coins appeared, the most important aspect was the weight. If a coin will have the same value as another, it must have the same weight. The coins were minted in precious metals, like gold or silver, and the weight aspect was crucial.
Aegina developed her own standard of weights, a little bit higher that the rest of the Greek world. For example, a drachm in Athens (“the attic standard”) had a weight of 4,31 g. and the aegian drahm had around 6,3 g. The reason for this 45 % heavier coin was that this standard was derived from the Phoenician one, used by the cities from Phoenicia.
The symbol of this coin was a turtle, seen from the upside, with its head up and tail down. On the other side the symbol as a “quadratum incusum” or incuse square, a typical reverse for the archaic period in ancient Greece, used from the 7th century until the 5th century.
During this time, “the turtles” kept the weight and the metal content at the same level. Also, because of the maintenance of the iconography, the coin was known by an increasing number of people and used in “international transactions”.
In 456 BC, Aegina was made member of the Delos League, an Athenian form of controlling the cities under its power. More, in 431 BC, at the beginning of the Peloponesian War, the population was expelled and replaced with Athenian colonists (klerurchs). During this time, Aegina minted no coins.
After the fall of the Athenian domination, Aegina minted again coins, similar with the previous ones. Only on the reverse, the letters A I G, in Greek, appeared, as the first 3 letters of the name of the city that minted this coins.
Shop now for $10 off first Purchase
Also, the sea turtle from the previous series was replaced by a land turtle. The artistic grade of execution is very high and the coin is a very attractive one.
As the city lost the economical power, the coinage was stopped during the 4th century BC. During the time of Alexander, the local mints produced tetradrach of Alexander type, with the symbol of the city, the turtle and the dolphin.
Stefan Vasilita.
Search the Coin Encyclopedia
Related Auctions
Related Articles
From time to time you will come across an ancient coin with a hole on it. Coins that were holed in ancient times are intriguing. Why was this so?
12th Mar 2018
The first bimetallic coins can be considered some private issues dating from the 4th century AD
11th Apr 2018
Learn about Roman Coins. Collecting Ancient Roman Coins Part I: An Introduction at Coins-Auctioned.com. Helping Roman Coin collectors and dealers from all over the globe.
10th Apr 2018
Latest Articles
Washington quarters are 25-cent US coins issued since 1932. The original obverse remains, with dozens of varieties and new reverses. Learn the history, types, key dates, and errors on the iconic coin!
4th Nov 2024
Walking liberty half dollars are 50-cent American coins circulated from 1916 to 1947. The iconic design has been featured on the silver eagle bullion since 1986 and remains sought-after by collectors.
7th Oct 2024
Standing liberty quarters were circulated US coins issued from 1916 to 1930 as part of the Renaissance of American Coinage. Learn the values, varieties, and stories of standing liberty quarters!
9th Sep 2024
Article Categories
Collection of articles providing lots of useful information on coins through the ages.
30 Articles





